The proton structure function F2 is related to the double differential cross section for inclusive ep scattering including photon and Z0 exchange via the following formula:
![]()
with ![]() .
. ![]() is the longitudinal
structure function,
is the longitudinal
structure function,
![]() is the parity violating term, and
is the parity violating term, and ![]() is the radiative
correction.
For comparison with other experiments we measure F2 containing
only contributions from virtual photon exchange.
Therefore we have to
absorb the contributions from the Z0 exchange in a correction factor
is the radiative
correction.
For comparison with other experiments we measure F2 containing
only contributions from virtual photon exchange.
Therefore we have to
absorb the contributions from the Z0 exchange in a correction factor
![]() . This
correction is 6% for the highest Q2 bin shown in this analysis and lower
for
all the other bins.
Also the corrections due to the longitudinal
structure function and the
radiative corrections are small (lower than 15% and 5% respectively), and
can be absorbed in correction factors
. This
correction is 6% for the highest Q2 bin shown in this analysis and lower
for
all the other bins.
Also the corrections due to the longitudinal
structure function and the
radiative corrections are small (lower than 15% and 5% respectively), and
can be absorbed in correction factors ![]() ,
from QCD prescriptions,
and
,
from QCD prescriptions,
and ![]() ,
from the HERACLES Monte Carlo.
This results in the following equation for F2:
,
from the HERACLES Monte Carlo.
This results in the following equation for F2:
![]()
To derive F2 from the observed double differential cross section, an unfolding method is used.
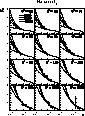
Figure 4: Proton structure function F2 as a function of x. The inner error bars show the statistical error only, while the outer bars show the statistical and the systematic error added in quadrature. Q2 is given in GeV2.
The results for the DA method are shown in figure 4. Our most important systematic check is the comparison of the values of F2 for the DA and the electron method. These two methods use overlapping data samples, but the reconstruction of the kinematic variables is largely independent. Within the statistical errors there is very good agreement between the two methods.