In zeroth order, F2 is constant in Q2
and the gluons do not contribute to the cross section.
The scaling violations, as shown in figure 5, are a higher
order process
(called leading order, LO, for our purpose).
At small values of x, x < 10-2, they are dominated
by quark pair production from gluons leading to positive scaling violations with increasing Q2.
Therefore the gluon momentum density, xg(x,Q2), can directly be extracted
from the slope ![]() .
.
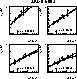
Figure: Scaling violation of the proton structure function F2 as a function of Q2 for fixed values of x as given in the figure.
The solid lines show a straight line fit, while the dashed lines show the result of the global NLO fit. The arrows indicate Q2 = 20 GeV2.
We compare different methods, the approximate method of Prytz [5], EKL [6], and a fit making use of the full NLO GLAP [7] evolution equation.
The method of Prytz uses the approximation that at low values of x the GLAP evolution equation is dominated by the gluonic terms. Consequently the quark splitting functions are neglected and only the gluon splitting functions are considered. Using a LO result for Pqg, the gluon splitting function and making a Taylor expansion of the gluon momentum density zg(z,Q2) at z=x/2 results in the following equation in LO:
where the gluon density at x is calculated from the slope of F2 at x/2.
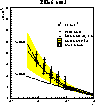
Figure 6: Gluon momentum density as a function of x at Q2 = 20 GeV2
Equation 4 has been extended to NLO, still neglecting quark contributions. In the NLO GLAP fit, all the F2 data from ZEUS taken in 1993 have been used. To make a constraint at large values of x, NMC data [8] on F2 were included. The fit of the parton momentum distributions as a function of x has been performed at a value of Q20 = 7 GeV2 assuming a functional form of the parton distribution as used by many parametrisations [4].
The power of the rise of the gluon momentum density
with decreasing x has been calculated
and found to be ![]() .
.
The results from the global fit, from the method of Prytz and from that of EKL are shown in figure 6 for Q2 = 20 GeV2. The shaded band shows the error on the global fit. The inner error bars on the points show the statistical error only, while the outer error bars show the statistical and the systematic error added in quadrature. A good agreement between all methods is observed.